An operator is a symbol that the compiler uses to know when to do a mathematical or logical operation.
Types of Operators in Arduino
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Boolean Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Compound Operators
Arithmetic Operatos
| Operator Name |
Symbol |
Description |
| Assignment Operator |
= |
store a value to a variable |
| Addition |
+ |
Add two operand |
| Subtraction |
- |
subtracts second operand from the first |
| Multiplication |
* |
Multiplies both operands |
| Division |
/ |
Divide Numerator by denominator |
| modulo |
% |
Divide Numerator by denominator to get remainder |
Example
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
void setup(){
//nothing to setup
}
void loop() {
int x=9,y=4,z;
//addition
z=x+y;
//substraction
z=x-y;
//multiplication
z=x*y;
//Division
z=x/y;
//modulus
z=x%y;
}
|
Comparison Operators
| Operator Name |
Symbol |
Description |
| Equal to |
== |
check to see whether the values of two operands are the same ie A==C |
| Not Equal to |
!= |
it becomes true when values of two operands are not equal |
| Less than |
< |
checks whether the left operand is less than right operand value |
| Less than or equal to |
<= |
Multiplies both operands |
| Greater Than |
> |
check whether the value in left operand is greater than the one in right |
| Greater than or equal to |
>= |
checks whether the value in the left operand is greater or equal to the right one |
Boolean Operators
| Operator Name |
Symbol |
Description |
| AND |
&& |
logical AND |
| OR |
` |
|
| NOT |
! |
it is used to reverse the logical state of its operands |
Example
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
void loop(){
int a=0; c=2;
bool d=false;
//and operator
if((a>c) && (c<a)) {
//do something
}
//or operator
if((a>c) || (c==a)) {
//do something
}
//NOT operator
if(!(a>c)) {
//do somethinh
}
}
|
Bitwise Operators
Bitwiseand (&)
- It is represented by a single ampersand
- It is used between two integer expressions.
- The rule of AND is:if both input bits are 1, the resulting output is 1, otherwise the output is 0.
- Check this example:
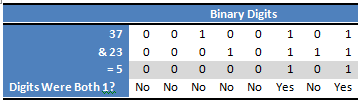
Example
1
2
3
4
|
int a = 92; // in binary: 0000000001011100
int b = 101; // in binary: 0000000001100101
int c = a & b; // result: 0000000001000100, or 68 in decimal.
|
Bitshiftleft(«)
- it causes the left operand’s bits to be shifted left by the number of positions indicated by right operand.
1
2
3
|
int a = 5; // binary: 0000000000000101
int c = a << 3; // binary: 0000000000101000, or 40 in decimal
|
- Also note that as you shift the bits, the left most ones shifts out of existence.
Bitshiftright(»)
-Unlike Bitshiftleft, the bits of the left operand are shifted to the right by the number of positions indicated by right operand.
1
2
|
int a = 40; // binary: 0000000000101000
int b = a >> 3; // binary: 0000000000000101, or 5 in decimal
|
Bitwisexor(^)
- Also known as Exclusive OR.
- It is written using carret symbol (^)
- A bitwise XOR operation results in a 1 only if the input bits are different, else it results in a 0.
Example
1
2
3
4
|
int x = 12; // binary: 1100
int y = 10; // binary: 1010
int z = x ^ y; // binary: 0110, or decimal 6
|
Bitwiseor
-Represented with vertical symbol ‘|’.
- The bitwise OR of two bits is 1 if either or both of the input bits is 1, otherwise it is 0.
Example
1
2
3
|
int a = 92; // in binary: 0000000001011100
int b = 101; // in binary: 0000000001100101
int c = a | b; // result: 0000000001111101, or 125 in decimal.
|
Bitwisenot
- Represented with tilde character ‘~’.
- It is applied on only single operand.
- it changes a bit to opposite of itself
Example
1
2
3
4
|
int a = 103; // binary: 0000000001100111
int b = ~a; // binary: 1111111110011000 = -104
|
Compound Operatos
| Operator Name |
Symbol |
Description |
| Increment |
++ |
Raises the integer value by one |
| decrement |
- - |
Decrements the integer value by one |
| Compound addition |
+= |
add right operand to the left and assigns the result to the left operand |
| Compound Subtraction |
-= |
it subtracts the right operand from the left and assigns the result to the right operand |
| Compound Multiplication |
*= |
It multiplies the right operand with the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand |
| Compound Division |
/= |
it divides left operand with the right and then assigns the result to the left operand |
| Compound Modulo |
%= |
It find the remainder by dividing left operand and right operand and assigns the result(remainder) to the left operand |
Example
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
void loop(){
int a =10;
int b=20;
int c=0;
//increment
a++
//decrement
a--
//compound addition
b+=a;
//compound subtraction
b-=a;
//compound Multiplication
b*=8;
//Compound division
b/=3;
//Compound Modulus
b%=2;
}
|
